동기화를 위해 Lock을 한단 개념은 다들 알고 있을 것이다.
이때, Lock의 범위를 지정해 줄 수도 있는데, class / instance 로 나누어 볼 수 있다.
| Object level lock | Class level lock | |
|---|---|---|
| static | non - staic 데이터를 thread safe하게 만들 때 사용 | static 데이터를 thread safe하게 만들기 위해서 사용 |
| 범위 | 클래스의 모든 인스턴스가 각자의 lock을 가질 수 있다. | 클래스 하나당 하나의 lock만 존재한다. |
public class ObjectLevelLockExample {
public void objectLevelLockMethod() {
synchronized (this) {
}
}
}
public class ClassLevelLockExample {
public void classLevelLockMethod() {
synchronized (ClassLevelLockExample.class) {
}
}
}
1️⃣ Object level lock
🔽 예제 1) 인스턴스 한개 / 두개 생성에 따른 차이
public class A {
public synchronized void run(String name) {
System.out.println(name + "락 걸기");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(name + "락 해제");
}
}
public class hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A(); // 인스턴스는 하나.
Thread thread1 = new Thread( () -> {
a.run("thread-1");
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread( () -> {
a.run("thread-2");
});
thread1.start(); // 쓰레드 2개
thread2.start();
}
}
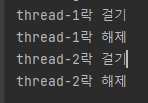
✅ 결과 - 쓰레드 별로 lock을 획득/반납
